
Presence of a bleb (white raised circle)ġ5. The presence of the weal or bleb indicates that the medication is in the dermis. Once syringe is in place, slowly inject the solution while watching for a small weal or bleb to appear.
Im injection sites skin#
Keeping the bevel side up allows for smooth piercing of the skin and induction of the medication into the dermis. Insert the needle only about 1/4 in., with the entire bevel under the skin. Place the needle almost flat against the patient’s skin, bevel side up, and insert needle into the skin. Hold syringe at a 5- to 15-degree angle from the site. This allows for easy handling of the syringe. Hold the syringe in the dominant hand between the thumb and forefinger, with the bevel of the needle up. Taut skin provides easy entrance for the needle.

Using non-dominant hand, spread the skin taut over the injection site. This decreases risk of accidental needle-stick injury. Remove needle from cap by pulling it off in a straight motion. Allowing the skin to dry prevents introducing alcohol into the tissue, which can be irritating and uncomfortable. Pathogens from the skin can be forced into the tissues by the needle. Clean the site with an alcohol swab or antiseptic swab. Gloves help prevent exposure to contaminants. Perform hand hygiene and apply non-sterile gloves. Selecting the correct site allows for accurate reading of the test site at the appropriate time.
Im injection sites free#
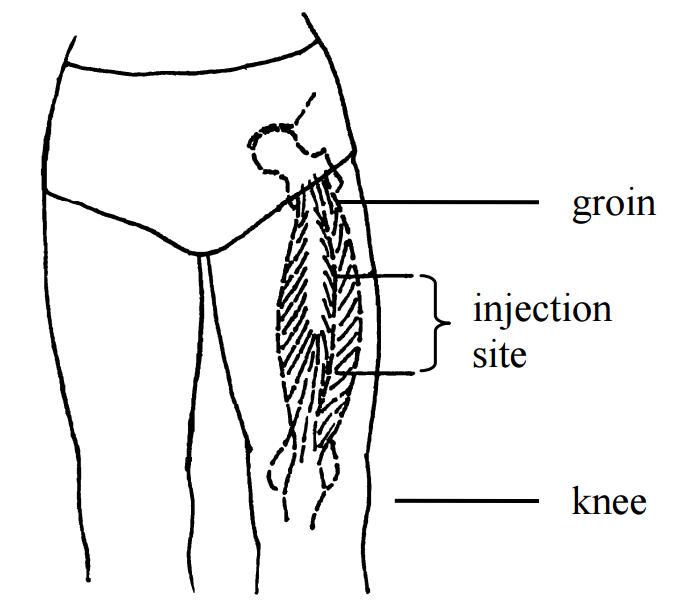
Site should be free from lesions, rashes, and moles. Assist the patient to the appropriate position as required. Select appropriate site for administration. Assess patient for any contraindications to the medications.Īssessment is a prerequisite for every medication given.ħ. Two patient identifiers are patient name and date of birth. This ensures accuracy of the medication or solution and prevents errors. Compare MAR to patient wristband and verify this is the correct patient using two identifiers. Close the door or pull the bedside curtains.ĥ. Enter room and introduce yourself, explain procedure and the medication, and allow patient time to ask questions.Įxplaining rationale increases the patient’s knowledge and reduces their anxiety.Ĥ. Gather all supplies: medication syringe, non-sterile gloves, alcohol swab and sterile gauze, Band-Aid (if required). Compare physician orders and MAR Prepare medication from a vialĢ. Preparing medications ensures patient safety with medication administration. Properly identifying medication decreases risk of inadvertently administering the wrong medication.
Im injection sites manual#
Check physician orders, Parenteral Drug Therapy Manual (PDTM), and MAR to validate medication order and guidelines for administration. Ensure all medication is properly identified. Prepare medication or solution as per agency policy. Re-verify order with physician if appropriate.ġ.
Always take steps to eliminate interruptions and distractions during medication preparation.It is not necessary to aspirate because the dermis is relatively without vessels.

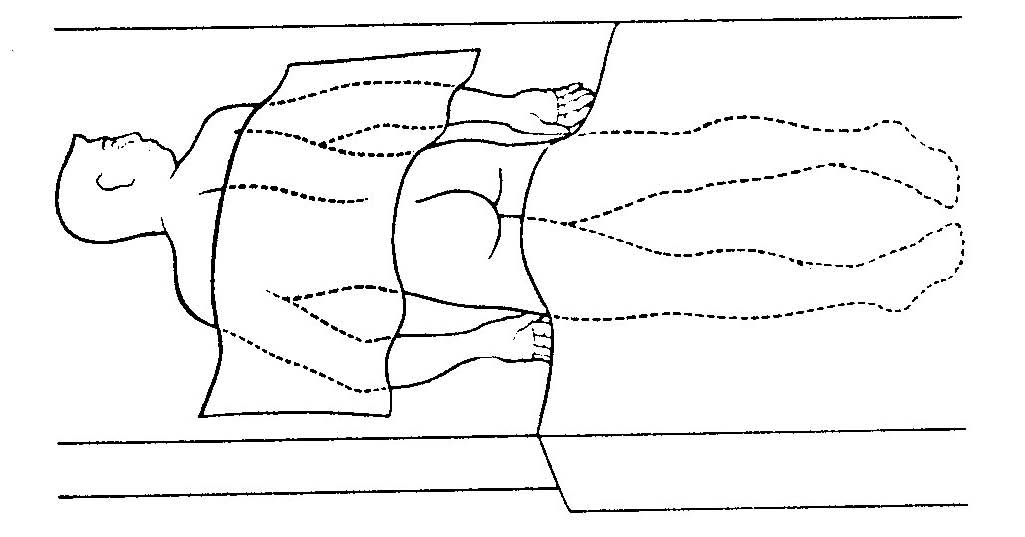
Figure 7.13 TB syringe Checklist 56: Administering an Intradermal (ID) Injectionĭisclaimer: Always review and follow your hospital policy regarding this specific skill. Once the ID injection is completed, a bleb (small blister) should appear under the skin. Checklist 56 outlines the steps to administer an intradermal injection. The angle of administration for an ID injection is 5 to 15 degrees. The dosage of an ID injection is usually under 0.5 ml. Choose an injection site that is free from lesions, rashes, moles, or scars, which may alter the visual inspection of the test results (Lynn, 2011).Įquipment used for ID injections is a tuberculin syringe calibrated in tenths and hundredths of a millilitre, and a 1/4 to 1/2 in., 26 or 27 gauge needle. The most common sites used are the inner surface of the forearm and the upper back, under the scapula. The advantage of these tests is that the body reaction is easy to visualize, and the degree of reaction can be assessed. These types of injections are used for sensitivity tests, such as TB (see Figure 7.13), allergy, and local anesthesia tests. The ID injection route has the longest absorption time of all parenteral routes. Intradermal injections (ID) are injections administered into the dermis, just below the epidermis. 7.3 Intradermal and Subcutaneous Injections


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
